Repeat Purchase Rate (RPR) Calculator
Calculate your Repeat Purchase Rate (RPR) with this online calculator. Discover the percentage of customers who make repeat purchases, gain insights into your retention performance, and benchmark against industry standards to inform your customer loyalty strategies.
Calculate your Repeat Purchase Rate & LTV ⬇️
Refine with Lifetime Value
Discover how Vision Labs can help you enhance key metrics like LTV and RPR with personalized strategies!
Visit VisionLabs.com/contact to start transforming your retention strategy.
Talk soon,
JJ Reynolds
Founder | Vision Labs
What is a good Repeat Purchase Rate?
While ideal RPR varies by industry and product type, here are some general guidelines:
- For frequently purchased items: Aim for an RPR of 20-25% within 90 days.
- For durable goods: A 12-15% RPR over a year might be considered strong.
Remember, context is key. Use these figures as a starting point and adjust based on your specific business model.
Here some things you can analyze in your Repeat Purchase Rate:
- Analyze trends over time: Look at how your RPR changes month-to-month or quarter-to-quarter. Is it increasing, decreasing, or stable? This can indicate the effectiveness of your retention efforts.
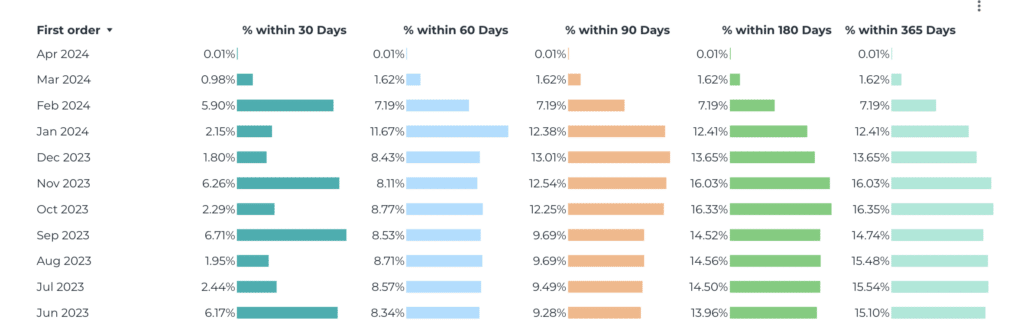
- Analyze Repeat Purchase Rate by cohorts: Break down RPR by customer cohorts (e.g., acquisition date, source, or demographics).
This reveals:
- Which cohorts have higher RPR: Did customers acquired during a specific campaign or product launch show better loyalty?
- How RPR evolves: Do newer cohorts have higher or lower RPR compared to older ones?
- Seasonal patterns: Are customers acquired in certain months more likely to make repeat purchases?
3. Identify actionable insights:
- High RPR cohorts: What can you learn from these groups to improve retention across the board?
- Low RPR cohorts: These may need targeted retention campaigns or improved onboarding.
- Sudden changes: A drop in RPR for recent cohorts might signal issues with product quality or customer experience.
4. Connect with other metrics: Combine RPR insights with metrics like Customer Lifetime Value or Average Order Value to get a comprehensive view of customer behavior and value.
How to calculate Repeat Purchase Rate in ecommerce? Formula included
To Calculate RPR follow these 5 steps:
- Choose a specific time period (e.g., 30 days, 2 months)
- Count total customers who made any purchase in this period
- Count customers who made more than one purchase in this same period
- Divide customers with multiple purchases by total customers
- Multiply the result by 100 to get a percentage
Repeat Purchase Rate Formula: RPR = (Number of Customers Who Made Multiple Purchases / Total Number of Customers) x 100%
Example of calculating RPR:
- Time period: January 1 to February 28 (2 months
- Total customers who made at least one purchase in this period: 100
- Customers who made more than one purchase in this same period: 250
- RPR = (250 / 1000) x 100% = 25%
Result: From January 1 to February 28, 25% of customers made repeat purchases.
What is Repeat Purchase Rate (RPR?
Repeat Purchase Rate (RPR) is a key metric that measures the percentage of customers who return to make additional purchases within a specific time frame. By tracking RPR, you can identify critical touchpoints where customers decide to return, uncover potential drop-off points, and optimize the path to repeat purchases.
Remember that RPR can vary significantly depending on your product type and its natural purchase frequency.
For instance, a high RPR for monthly subscription boxes might be expected, while a lower RPR for durable goods like appliances could still indicate strong customer satisfaction
FAQ's
What factors influence Repeat Purchase Rate?
RPR doesn't exist in a vacuum—it's shaped by various elements of the customer experience and the nature of your product or service. Key factors include:
- Natural Frequency: The inherent repurchase cycle of a product or service (e.g., high for groceries, low for appliances).
- Product Quality and Customer Service: Consistently high-quality products and positive customer interactions drive loyalty.
- Marketing Strategies and Personalized Offers: Effective retention campaigns and tailored recommendations encourage additional purchases.
- Overall Customer Experience: A seamless journey from purchase to post-sale support encourages returns.
- Pricing and Value Perception: Competitive pricing and perceived value for money influence repurchase decisions.
How frequently should you analyze Repeat Purchase Rate (RPR)?
However, the ideal frequency may vary depending on your business model, product type, and sales cycle. We usually break it down into 30, 60, 90, 180, and 365-day intervals to uncover patterns across different timeframe
For businesses with shorter purchase cycles or those implementing new retention strategies, more frequent analysis (e.g., monthly) might be beneficial. For businesses with longer purchase cycles, quarterly reviews might be sufficient.

JJ Reynolds
JJ Reynolds is the founder of Vision Labs, a white-label data agency specializing in custom measurement systems and real-time marketing dashboards. Having worked with startups to multi-billion dollar companies, he creates bespoke reporting solutions that help businesses turn data into decisions. His expertise in media buying, PPC, and analytics enables companies of all sizes to make smarter, data-driven choices.
All Marketing calculators
Get notified immediately as new calculators & strategies are launched
Join 6,000+ D2C Brands, Marketers, & Analysts who want to act on their data